
Now there are many different marketing channels that people from the sphere should orient and understand. To make things easier, we suggest understanding how evolution came to Web 3.
By seamlessly integrating blockchain, NFTs, and decentralized platforms, Web3 Marketing empowers businesses to forge deeper connections, foster transparency, and unlock unparalleled growth. In this article, ‘we’ll explore Web3 Marketing, uncovering its potential to revolutionize customer interactions and reshape the marketing terrain.
Join us as we navigate the exciting possibilities and strategies that will drive success in this new frontier.
Brief History Of Web Marketing
Web marketing has a rich history. It developed with the Internet itself. In the 1990s, businesses considered its potential as a marketing tool. The first online ads – banners emerged during this time. The late 1990s saw the rise of search engines like Yahoo and Google, prompting the advent of search engine optimization as a critical strategy for improving website visibility.
In the 2000s, email marketing grew, allowing businesses to directly reach their target audience. Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising gained recognition, enabling advertisers to pay only when users clicked on their ads. Friendster and MySpace became the first social media platforms of the time.
As smartphones became ubiquitous, mobile marketing gained traction, emphasizing responsive website design and location-based advertising. The mid-2010s introduced content marketing as a way to provide valuable information to audiences, fostering trust and engagement. Video marketing also surged, with YouTube and platforms like Vine capturing user attention.
Recent years have seen artificial intelligence (AI) integration in marketing automation, NFT developing, personalizing user experiences, and streamlining campaigns. Influencer marketing has leveraged individuals’ online influence to promote products and services.
The history of web marketing is a journey of adapting to technological advancements and changing user behaviors. From static banner ads to immersive multimedia experiences, web marketing continues to evolve, reflecting the dynamic nature of the digital landscape.
Web marketing history can be divided into three parts. ‘We’ll talk about each of them in the next section.
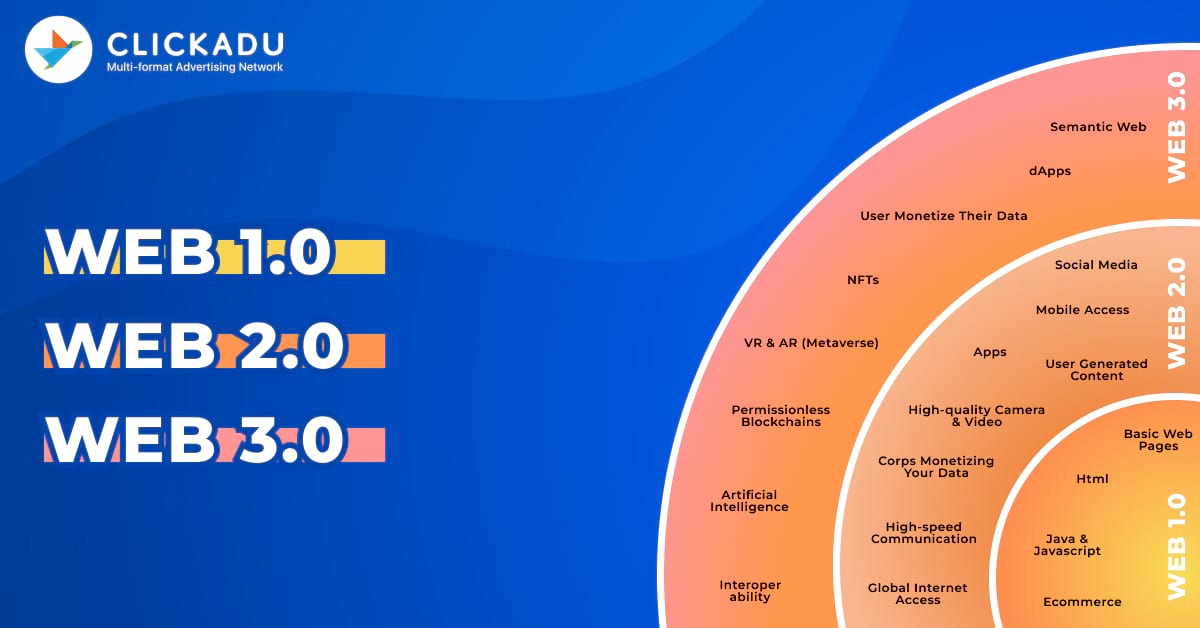
WEB 1
Web 1.0 was the early phase of the World Wide Web’s development. During 1980 – 2000, the internet was an information repository with limited interactivity and user-generated content. Websites were static and one-way, delivering information to users without much room for user engagement or participation.
Key characteristics of Web 1.0 include:
- Static content: websites were composed of static HTML pages that presented information one-dimensionally. The interactivity or dynamic content was little.
- Limited User Interaction: users can only consume the content presented on websites. The interaction was limited to clicking on links to navigate between pages.
- Basic Graphics: graphics and images were basic and often served primarily as decorative elements rather than integral parts of the user experience.
- Slow Connection Speeds: Internet connection speeds were relatively slow, which influenced the design of websites to be lightweight and focused on delivering content efficiently.
- Limited Search Capabilities: early search engines like Yahoo! and AltaVista helped users find information, but search results were often less accurate and relevant than today’s search engines.
WEB 2
This era introduced dynamic, interactive, and user-centric online experiences. User-generated content and social networking developed rapidly. Web 2.0 completely changed ‘people’s interaction with the Internet and with each other.
In the Web 2.0 period, marketers started using metrics such as cost of customer acquisition (CAC), customer lifetime value (LTV), cohorts, and so on. The work was based on principles that can be quantified in different areas.
The most important highlights during the lifetime of Web 2 are:
- User-Generated Content: Websites and platforms encourage users to actively contribute content. Blogs, forums, wikis, and social media platforms developed rapidly.
- Social Networking: Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn revolutionized online communication. Users were able to connect, share updates, and build digital relationships.
- Web Apps: web-based applications allow users to use software directly through web browsers, eliminating the need for desktop installations.
- Personalization: Websites began to tailor content based on user preferences and behavior, enhancing the user experience and engagement.
- E-Commerce Evolution: Online shopping has become simpler and smarter, with e-commerce platforms offering personalized recommendations and streamlined checkout experiences.
- Mobile and Responsive Design: The development of smartphones led to the rise of mobile-responsive websites and apps, ensuring consistent experiences across various devices.
WEB 3
Web 3.0, often called the”decentralized web,” did major improvements to the internet beyond its static and social phases. The main points of Web 3.0 marketing are blockchain, decentralized platforms, and AI.
Key features of the Web 3 era are:
- Decentralization: Web 3.0 embraces decentralized technologies like blockchain to distribute control and ownership, reducing reliance on centralized authorities. This empowers users and enhances security.
- Enhanced Privacy: Web 3.0 emphasizes user privacy and data ownership. Users got greater control over their personal information.
- AI Integration: Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are integrated to enhance user experiences. It helps to personalize content, automate tasks, and much more.
- NFTs and Digital Assets: Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) enable ownership and provenance tracking of digital assets. The rules of trading digital art, collectibles, and content are already changed.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: Web 3.0 integrates virtual and augmented reality technologies. It helps to create immersive online experiences that bridge the gap between the digital and physical worlds
AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the major changes in the Web3 era. As blockchain, decentralized platforms, and enhanced data interoperability shape the digital realm, AI emerges as a powerful tool that can elevate marketing strategies to new heights of effectiveness and personalization.
Artificial intelligence helps people in many spheres and will be able to do much more in the future as technology grows. AI enables enhanced data analysis to process vast amounts of data from decentralized sources and create predictive analytics based on ‘users’ behavior and historical data.
Artificial intelligence can create content – text, pictures, videos, and much more. Moreover, chatbots and virtual assistants empowered by AI can perform real-time conversations, offering instant assistance, recommendations, and information, enhancing customer experiences.
There are much more fields in which AI can be useful, like fraud detection, semantic understanding, personalization, and many others. However, integrating AI into Web3 marketing also presents challenges, such as data privacy concerns, algorithmic biases, and the need for continuous learning and adaptation. As AI-driven Web3 marketing evolves, businesses must strike a balance between technology’s capabilities and ethical considerations.
Decentralization
Web 3 is now actively working with the opportunities provided by decentralization. Decentralization allows the transfer of information from centralized systems and organizations to networks where the information belongs to no one.
Large organizations own information that can later be used to improve and optimize communication or other interaction. However, the critical point is that no one owns such volumes in decentralized networks and platforms.
Decentralized organizations are empowered to establish and sign smart contracts that achieve this. In that case, the data is stored in the blockchain.
Smart contracts are an integral and important part of the work. Web 3.0 mechanics and the basic concepts are built around these points.
NFT
The NFT is one of the Web 3 marketing mechanics that is based on the concept of smart contracts.
The NFT ‘isn’t exactly new mechanics. Traditional Web 2 organizations use NFT to modify brand creation and operation scenarios. Working with the NFT can serve different marketing purposes. In other words, the NFT is the part of the IP that is stored on the blockchain.
NFT can be used in the following cases:
- Increasing brand awareness;
- Creating something new and exclusive;
- Loyalty boosts;
- Charity promotion.
Metaverse
The concept of the Metaverse, a digital universe where individuals interact, create, and conduct various activities, rapidly evolves in the Web3 era. This emerging Metaverse is characterized by its decentralized nature, fueled by blockchain technology and the principles of Web3. Unlike its predecessors, the Web3 metaverse is not confined to a single virtual world but encompasses a network of interconnected digital spaces that transcend geographical and virtual boundaries.
Central to the Web3 metaverse is the idea of user ownership and control. Through blockchain and NFT technology, individuals gain true ownership of digital assets, from virtual real estate to unique items, artwork, and more.
Through mechanics and technology, Web 3 can improve Metaverse scenarios. However, this requires some difficult steps and obstacles to be carried forward. Metaverse projects in this period develop into a new generation.
The Web3 metaverse represents a revolutionary blend of technology, creativity, and human interaction. As it continues to evolve, it promises to reshape how we experience digital spaces, transcending the virtual and physical boundaries, and offering a glimpse into the limitless possibilities of the interconnected future.
Security And Identity
Digital identification and protection are used to identify a person in a digital space. This includes electronic logins, passwords, and other unique personal information. For example, digital identification is used for full-fledged web travel to access online services or platforms.
By the way, the system is not yet ideal, as users can often face data breaches and compromises. It is during Web 3 that mechanics are developed that can provide cybersecurity on a decentralized platform for digital identity management.
Criticism of WEB3
Many have noted that criticism of the decentralized system in Web 3 is growing, even though such work on the Internet is called democratized.
Centralization ‘hasn’t gone away yet. Web 3 is fully operational with support for smart contracts, Metaverse, tokens, and the NFT, but it is all pooled around centralized platforms. Because of this, decentralized, centralized protocols and applications will not always be reliable.
The second criticism was scalability. It is still an obstacle to blockchain and Web 3. As a result, a large number of protocols are threatened by decentralization and security. When providing poor quality moments in the aggregate, this results in centralization.
Bad UI/UX is another object that needs to be modified and improved. Many users lack user interface and experience. Unfortunately, on the Internet, you can find that if the site or application is very convenient, it is not safe to use.
Key Takeaways: WEB3 Digital Marketing
Web 3.0 is built on data privacy for users. In the future, users will have more control over their unique data. This leads to several problems in the work of marketers because they are used to using data to attract and retain customers. Community marketing should be the main point of digital marketers if they want to stay on top.
Web 3 tries to ensure clear, secure, and efficient communication between users and computers through a semantic network. With the introduction of AI, search queries will be understandable, and users will be more satisfied. For organizations and marketers, this means one thing: the possibility of creating and promoting high-quality interactive advertising.
Leaving out the details of the constant rapid development of Web 3, it is still at an early stage and moving a little forward. Digital marketers need to be prepared for changes in the system of work, trends, and so on.
Incorporating Web3 principles into digital marketing strategies can revolutionize customer interactions, enhance transparency, and create more value-driven, user-centric marketing experiences. However, navigating this new landscape requires adaptability, creativity, and a keen understanding of the evolving digital ecosystem.
Table of Contents